How to Choose the Right Domestic Battery Energy Storage System for Your Home
As the global demand for sustainable energy solutions continues to rise, homeowners are increasingly considering the benefits of Domestic Battery Energy Storage systems. These systems not only allow for better energy management and cost savings but also contribute to a more reliable and resilient home energy supply. According to Dr. Emily Carter, a leading expert in renewable energy technologies, "Investing in Domestic Battery Energy Storage can significantly enhance your energy independence and reduce your carbon footprint."
When selecting the right battery storage system for your home, several critical factors need to be considered, including capacity, discharge rate, and compatibility with existing energy systems. With various options available on the market, potential buyers must navigate through technical specifications and features to find the system that best meets their needs. Understanding the fundamentals of Domestic Battery Energy Storage can empower homeowners to make informed decisions that align with their energy goals and financial investments.
Ultimately, choosing the appropriate Domestic Battery Energy Storage solution is not just about technology; it's also about envisioning a sustainable future for your home and the environment. With the right knowledge and guidance, homeowners can leverage these systems to create a more efficient and eco-friendly living space, thus participating actively in the transition to renewable energy sources.

Understanding Domestic Battery Energy Storage Systems
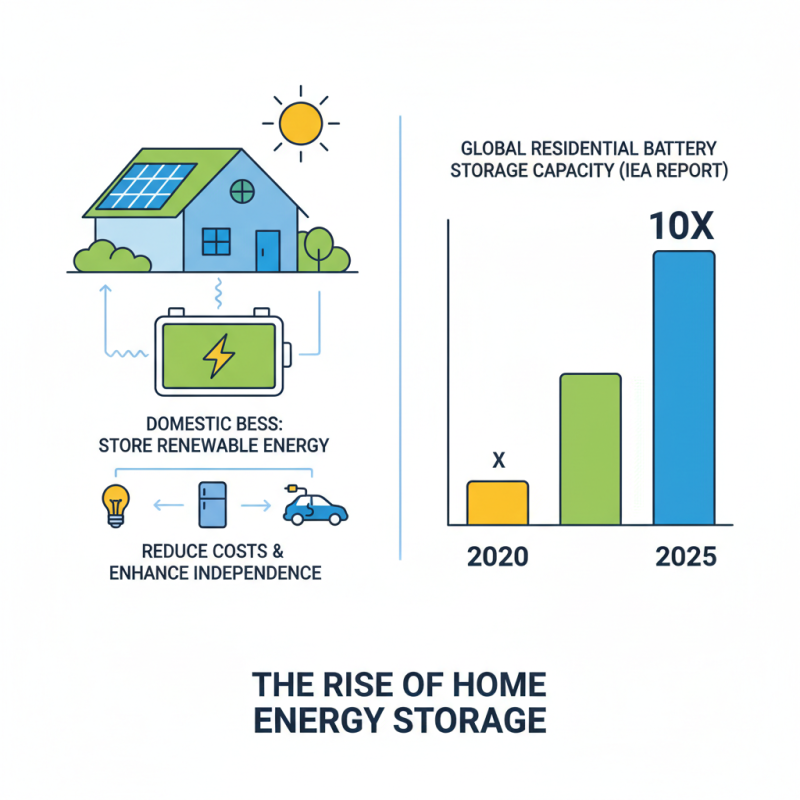
Domestic battery energy storage systems (BESS) have gained significant traction as homeowners seek ways to reduce energy costs and enhance energy independence. These systems store electricity generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels, for later use, thus contributing to a more resilient energy supply for households. According to a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), global installed capacity of residential battery storage systems is projected to increase tenfold from 2020 to 2025, highlighting the growing interest in energy storage solutions.
Understanding the key components of domestic battery energy storage systems is essential for making an informed choice. Typically, these systems consist of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, an inverter, and a management system that optimizes energy use. According to BloombergNEF, the cost of lithium-ion battery packs has fallen by 89% since 2010, allowing many homeowners to take advantage of this technology. When selecting a battery system, it is important to consider factors such as capacity, efficiency, cycle life, and warranty. Homeowners must assess their energy needs, analyze potential savings on electricity bills, and determine how much renewable energy is available at their location. With the right information, choosing the optimal domestic battery energy storage system can lead to significant energy savings and sustainability benefits.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Battery Storage System
When selecting a domestic battery energy storage system, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure the chosen system meets your needs. First and foremost, consider the capacity of the battery. This refers to the amount of energy the battery can store, which is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Assess your household energy consumption patterns to estimate how much storage is necessary to cover your daily usage or to power essential appliances during outages.
Another important factor is the discharge rate, which indicates how quickly the battery can release energy. A higher discharge rate can be vital for households with significant energy demands or those relying on the system during peak usage times. Additionally, pay attention to the battery's lifespan and warranty conditions, as these will provide insight into the long-term reliability and performance of the system. Evaluating the efficiency of the battery, which affects how much energy you can actually use versus what is lost in the process, will also help in selecting a system that maximizes your energy savings.
Lastly, consider the installation requirements and the available space in your home. Different systems may have specific space requirements, and their compatibility with your existing energy setup is crucial. Understanding these factors will help you make an informed decision, ensuring that the energy storage system you choose aligns with your energy needs and home infrastructure.
Different Types of Battery Technologies Available for Home Use

When selecting a domestic battery energy storage system, understanding the various battery technologies available is crucial for making an informed decision. Currently, the three primary types of battery technologies used for home energy storage are lithium-ion, lead-acid, and saltwater batteries. According to a recent industry report, lithium-ion batteries dominate the market, accounting for approximately 80% of home energy storage installations due to their high energy density and efficiency, with round-trip efficiencies typically above 90%. This makes them particularly attractive for homeowners looking to maximize solar energy use and reduce utility bills.
Lead-acid batteries, although older technology, still play a role in energy storage, especially for those seeking a cost-effective solution. They are generally less expensive upfront; however, they have a shorter lifespan and lower depth of discharge compared to lithium-ion batteries. A recent study indicated that while lead-acid batteries can cost about 50% less than their lithium-ion counterparts per kilowatt-hour, they only last about 3-5 years, compared to 10-15 years for lithium-ion. On the other hand, saltwater batteries are emerging as an alternative with environmentally friendly materials, boasting a longer lifespan and safety profile, although their market share remains small due to current energy density limitations. Research shows that while they are less efficient than lithium-ion systems, they may appeal to eco-conscious consumers and could grow as technology advances.
Ultimately, the choice of battery technology depends on individual needs, budget constraints, and long-term energy goals, making it essential to weigh the pros and cons of each option. As the energy storage market matures, advancements in technology are likely to further influence these dynamics, providing more efficient and affordable solutions for homeowners.
Evaluating Your Home’s Energy Needs and Usage Patterns
When evaluating your home’s energy needs and usage patterns, it's essential to assess your household's energy consumption. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average American home uses about 877 kWh per month. Understanding your daily energy usage can help you determine the size and capacity of the battery energy storage system that would be most beneficial. Taking note of peak usage times, such as evenings when families are typically home, can identify when you would benefit most from stored energy.
Tips: Start by analyzing your electricity bills over the past year to uncover patterns in consumption. You can utilize tools like energy monitors to gather more accurate, real-time data on your home’s energy needs.
In addition to understanding consumption, consider your future energy goals. If you plan to install solar panels, a battery system can store excess energy generated during the day for nighttime use. Data from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that homes with solar and battery systems can achieve over 90% energy independence, significantly lowering electricity costs. Evaluate how much energy storage you need based on factors like your solar production, battery efficiency, and potential outages in your area.
Tips: Consult local solar installers or energy experts for more personalized assessments that factor in weather variability and future energy prices. This approach will ensure you select an energy storage system tailored precisely to your needs.
How to Choose the Right Domestic Battery Energy Storage System for Your Home
| Energy Needs Dimension | Value (kWh) | Usage Pattern | Frequency (per day) | Peak Hours (Time) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lighting | 2 | Evening | 5 | 6 PM - 10 PM |
| Refrigerator | 1.5 | 24/7 | 1 | N/A |
| Heating/Cooling | 5 | Seasonal | 3 | 8 AM - 10 AM, 6 PM - 8 PM |
| Water Heater | 4 | Daily | 1 | 6 AM - 7 AM |
| EV Charging | 8 | Evening/Weekend | 1 | 7 PM - 11 PM |
Cost-Effectiveness and Incentives for Energy Storage Systems
When considering a domestic battery energy storage system, cost-effectiveness is a key factor that can heavily influence your decision. These systems not only allow homeowners to store energy generated from renewable sources, but they also provide financial benefits over time. By reducing reliance on the grid and decreasing energy bills, these systems can offer significant savings. It's important to evaluate the overall return on investment, which includes initial costs, installation, maintenance, and potential savings on electricity bills.
In addition to cost considerations, various incentives can make energy storage systems more affordable. Many governments and local authorities offer tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives to encourage the adoption of clean energy technologies. Researching available programs in your area can help you identify potential savings and financing options. These incentives can significantly lower the overall expenditure and speed up the payback period of your investment in energy storage. Therefore, it's crucial to understand both the upfront costs and the long-term financial incentives before making a decision on which battery energy storage solution is best suited for your home.
Cost-Effectiveness of Domestic Battery Energy Storage Systems
This chart illustrates the cost-effectiveness of various domestic battery energy storage systems based on initial cost, payback period, and annual savings.
Related Posts
-

7 Essential Tips for Maximizing Your Domestic Battery Energy Storage Efficiency
-

Exploring the Future of Home Pumped Hydro Storage for Sustainable Energy Solutions
-

Top Benefits of Domestic Commercial Battery Storage in 2025 You Need to Know
-

Unlocking the Future: How Solar Plant Battery Storage Can Revolutionize Renewable Energy
-

2025 Top Cryotex Massage Gun Charging Guide for Optimal Performance
-

Why You Need a Cryotex Massage Gun Charging for Optimal Muscle Recovery
