Understanding Residential Thermal Storage for Energy Efficiency Solutions
Residential thermal storage is an innovative solution aimed at enhancing energy efficiency in homes. It involves storing heat for later use, which can significantly reduce energy bills. This technology captures thermal energy during off-peak hours, using it when demand is high. Many homes can benefit from this approach, especially in regions with fluctuating temperatures.
The concept is relatively straightforward. Homes equipped with thermal storage systems can rely less on grid energy during peak times. Instead, they use stored heat to maintain comfortable living conditions. However, the implementation of residential thermal storage is not without challenges. Some homeowners may find the initial investment daunting. Questions about the effectiveness and maintenance of such systems may arise.
Understanding residential thermal storage requires careful consideration. The benefits can be substantial, yet the obstacles should not be overlooked. Individuals must weigh the pros and cons. Education on this technology helps homeowners make informed decisions. With the right approach, residential thermal storage can play a crucial role in shaping a sustainable future.
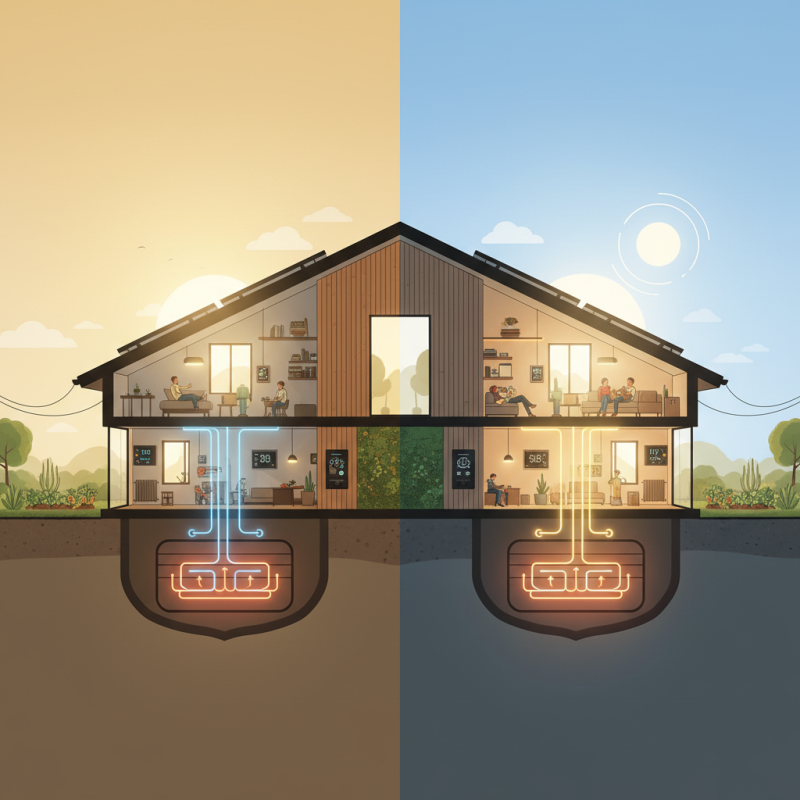

Overview of Residential Thermal Storage Systems
Residential thermal storage systems are designed to store energy for heating or cooling in homes. These systems can use materials like water or solid substances to retain and release thermal energy. They help balance energy use and reduce peak demand. This can lead to significant savings on energy bills.
One popular option is water tanks. They can store hot or cold water, making it easy to access when needed. Another choice is phase change materials. These materials can change states—solid to liquid—adding efficiency. Both methods can enhance home comfort and energy efficiency.
Tips: Consider the room size before installation. Proper sizing is crucial. Always evaluate home insulation. Better insulation can improve overall efficiency. Also, check local energy programs. They may offer incentives for thermal storage systems.
Types of Thermal Storage Technologies in Homes
Thermal storage technologies are essential for enhancing energy efficiency in residential spaces. One common method is water storage. Homes can use large tanks filled with hot water. This can be heated during off-peak hours. It holds the heat for later use. Some households may find they run out of hot water if usage spikes.
Another option is phase change materials (PCMs). These materials store thermal energy by changing states. For example, when they freeze or melt, they absorb or release heat. They can be installed in walls or ceilings. However, PCMs often have a high upfront cost. Homeowners may hesitate to invest if they don’t see immediate benefits.
Thermal mass, using materials like concrete or brick, acts as a natural heat sink. It absorbs heat during the day and releases it at night. While effective, homes with poor insulation might negate its benefits. Proper design is crucial for maximizing efficiency. Many people overlook this detail when planning renovations.
Understanding Residential Thermal Storage for Energy Efficiency Solutions
| Type of Thermal Storage | Size (kWh) | Efficiency (%) | Cost ($/kWh) | Main Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Tank Storage | 200 | 90 | 300 | Space heating, Domestic hot water |
| Phase Change Materials | 40 | 85 | 500 | Building materials, HVAC systems |
| Ice Storage | 150 | 80 | 400 | Cooling systems |
| Thermal Mass | Variable | Variable | N/A | Passive heating/cooling |
Benefits of Thermal Storage for Energy Efficiency
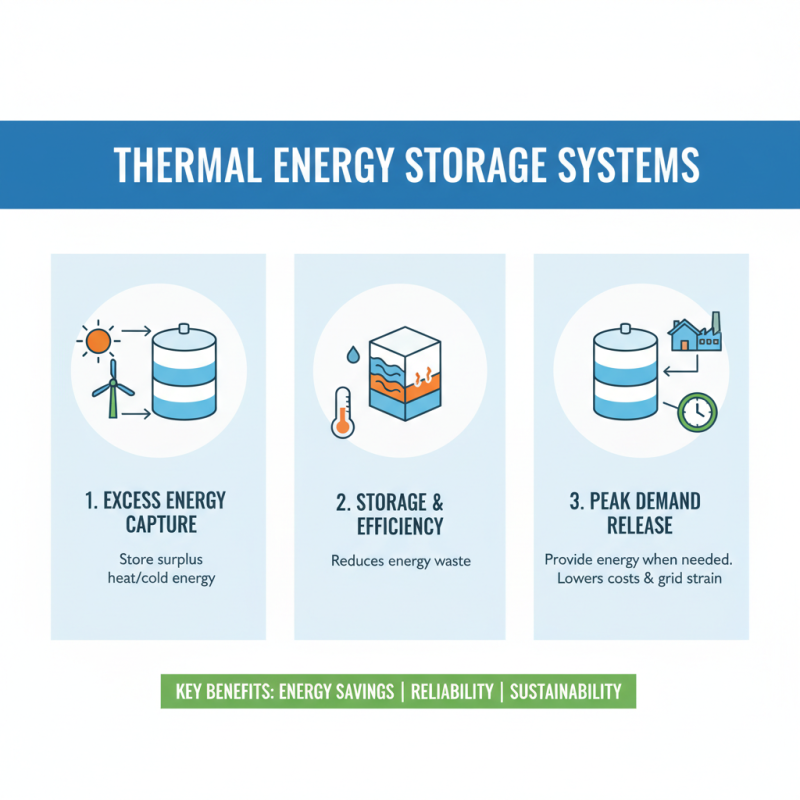
Thermal storage systems offer significant benefits for energy efficiency. By storing excess thermal energy, these systems can release it during peak demand times. This process helps reduce the need for additional energy sources, which can be costly and inefficient.
Residential thermal storage can manage heating and cooling loads effectively. For instance, homeowners can heat water or air during off-peak hours. They can then use that stored energy when electricity prices surge. This practice not only saves money but also decreases strain on the grid.
However, the integration of thermal storage systems can be complex. Homeowners must consider factors such as installation costs and efficiency ratings. Not all systems operate optimally in every home. A one-size-fits-all approach may lead to disappointment. It’s essential to research and understand the specifics before committing.
Integration of Thermal Storage with Renewable Energy Sources
Thermal storage systems offer a unique solution for integrating renewable energy sources. These systems capture excess energy produced during peak sunny or windy hours. They store heat or cold to be used later, balancing demand and supply effectively. This is crucial, as renewable energy production can be unpredictable.
When combined with solar panels, thermal storage can enhance energy efficiency. For instance, during the day, solar panels generate electricity, which can be used to heat a water tank. At night, this stored heat provides warm water without additional energy expenditure. However, the initial setup costs and maintenance can be a concern for many homeowners.
Embracing thermal storage requires careful planning. Some may overlook the right size for their systems, leading to inefficiencies. It's essential to assess energy needs accurately. A miscalculation could result in either wasted resources or insufficient heating. Continuous learning and adjustments are necessary to optimize thermal storage solutions with renewable sources.
Understanding Residential Thermal Storage for Energy Efficiency Solutions
Challenges and Future Trends in Residential Thermal Storage Solutions
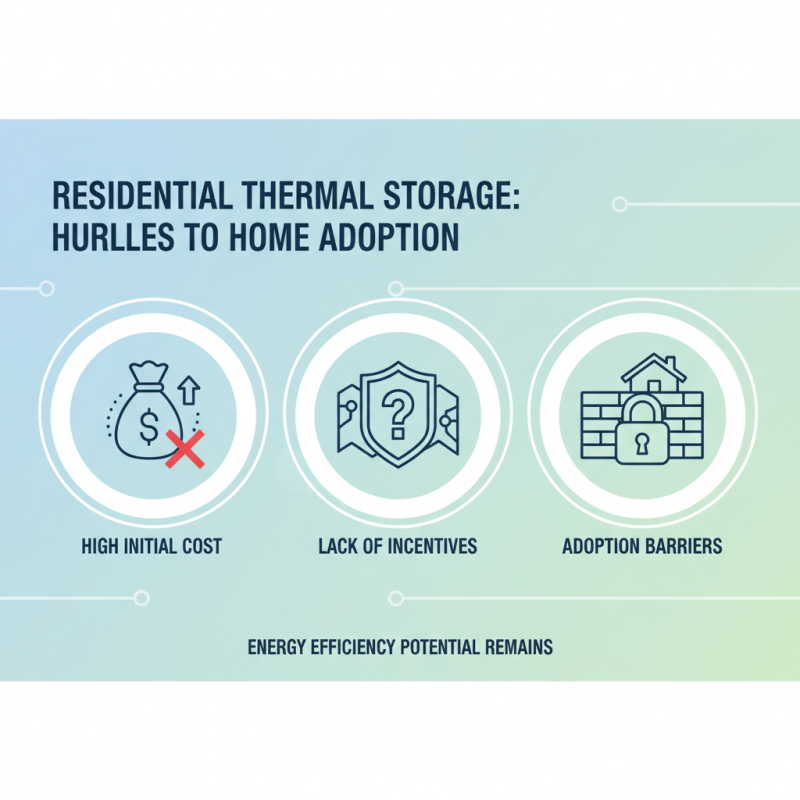
Residential thermal storage offers a promising solution to enhance energy efficiency in homes. However, there are significant challenges that must be faced. One major challenge is the initial cost of installation. Many homeowners hesitate due to high upfront expenses. Incentives can help, but not all areas offer them. This creates a barrier for adoption.
Another key issue is the lack of public awareness. Many residents are unaware of how thermal storage works. This leads to misconceptions about its efficiency and benefits. Educating the public is crucial. Workshops and information campaigns could bridge this gap. Yet, finding the right channels to reach homeowners remains a hurdle.
Future trends point towards improved technology. Developments in materials could enhance performance. Yet, the industry must address scalability. Solutions must be effective for various home sizes and types. Continuous research is vital. We should reflect on our strategies and explore innovative approaches. Only then can residential thermal storage truly thrive.
Related Posts
-
2025 Guide: How to Optimize Residential Thermal Storage for Energy Efficiency
-

Exploring Innovations in Homemade Solar Battery Storage at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Understanding the Importance of Solar Inverters and Battery Storage for a Sustainable Future
-

Unlocking the Benefits of Homemade Solar Battery Storage for Sustainable Living
-
How to Choose the Right Volt Evse Distribution for Your Charging Needs
-

Unlock Enhanced Recovery: How to Optimize Your Theragun Prime Charging Experience
